A new guide describes how builders can increase the structural and energy performance of a home with a raised-heel truss construction system. According to the publisher of the guide, APA – The Engineered Wood Association, building with raised-heel trusses results in savings for the builder and an energy-efficient, structurally superior residence for the homeowner. A raised-heel truss has a “heel” that extends up from the top of the wall and elevates the truss at the building’s edges. In other respects, it is identical to a conventional truss.
The guide says that raising the truss higher has two big advantages over typical truss construction: It simplifies attic ventilation, and it leaves ample room for insulation above exterior wall top plates. With the added space, the truss doesn’t compress attic insulation over the top plate and compromise its insulation value, a common weakness of conventional truss systems.
The energy code allows for use of less insulation for the entire ceiling system when a raised-heel truss system is used, allowing builders to reduce material costs and increase energy efficiency. Home Energy Rating (HERS) studies also indicate that with consistent ceiling insulation, APA says, the home maintains a more stable interior temperature that results in a more comfortable home and lower utility bills.
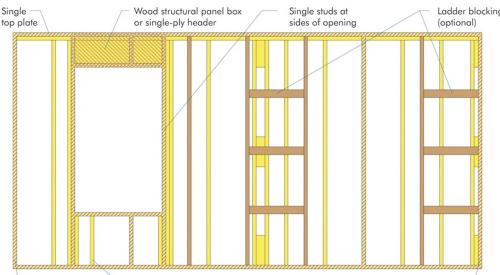
The system also features structural advantages, according to APA. Wall systems that combine raised-heel trusses with overlapping continuous plywood or oriented strand board (OSB) sheathing have better resistance to lateral forces produced by high winds or seismic activity than those fastened with conventional wall-to-truss connections.